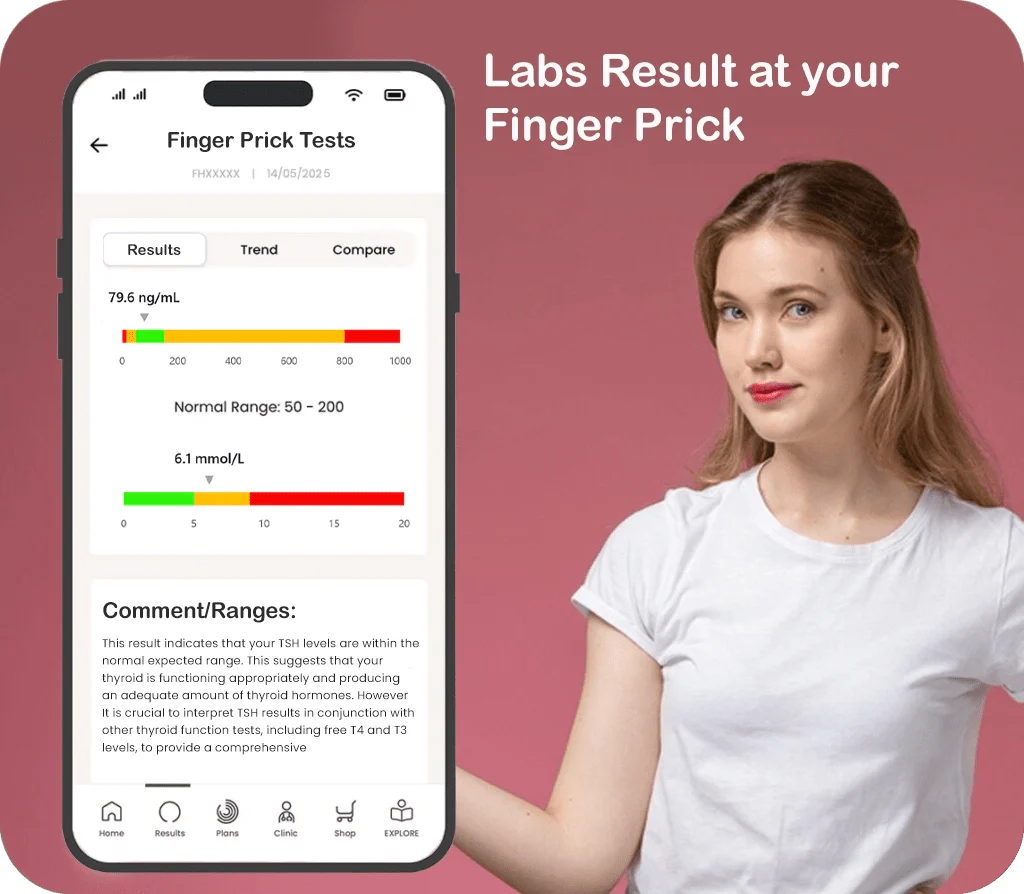
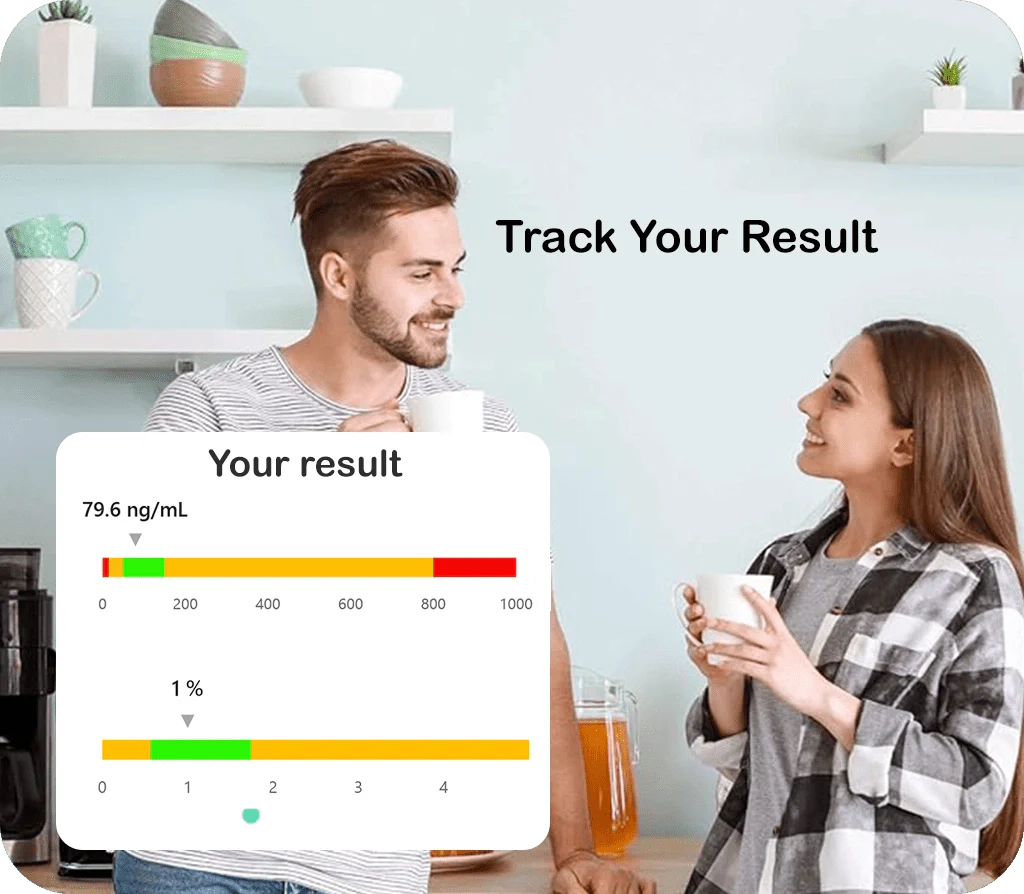
My Store
Core Rheumatology Assessment
Core Rheumatology Assessment
Ongoing joint pain, stiffness, or swelling could be early signs of autoimmune or inflammatory joint disorders. The Core Rheumatology Assessment is designed to help detect common causes of joint inflammation, including rheumatoid arthritis and gout, by measuring key autoimmune and metabolic markers. It’s an essential screening tool for those with persistent joint symptoms or a family history of rheumatic disease.
Couldn't load pickup availability


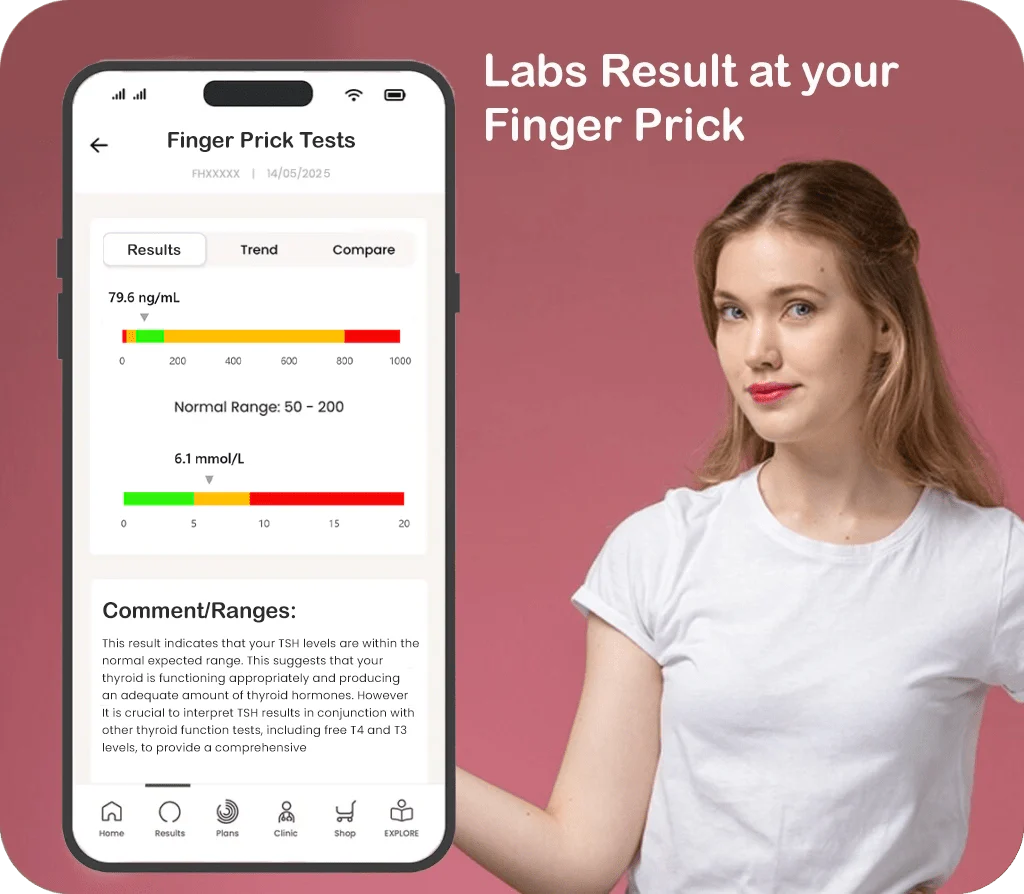
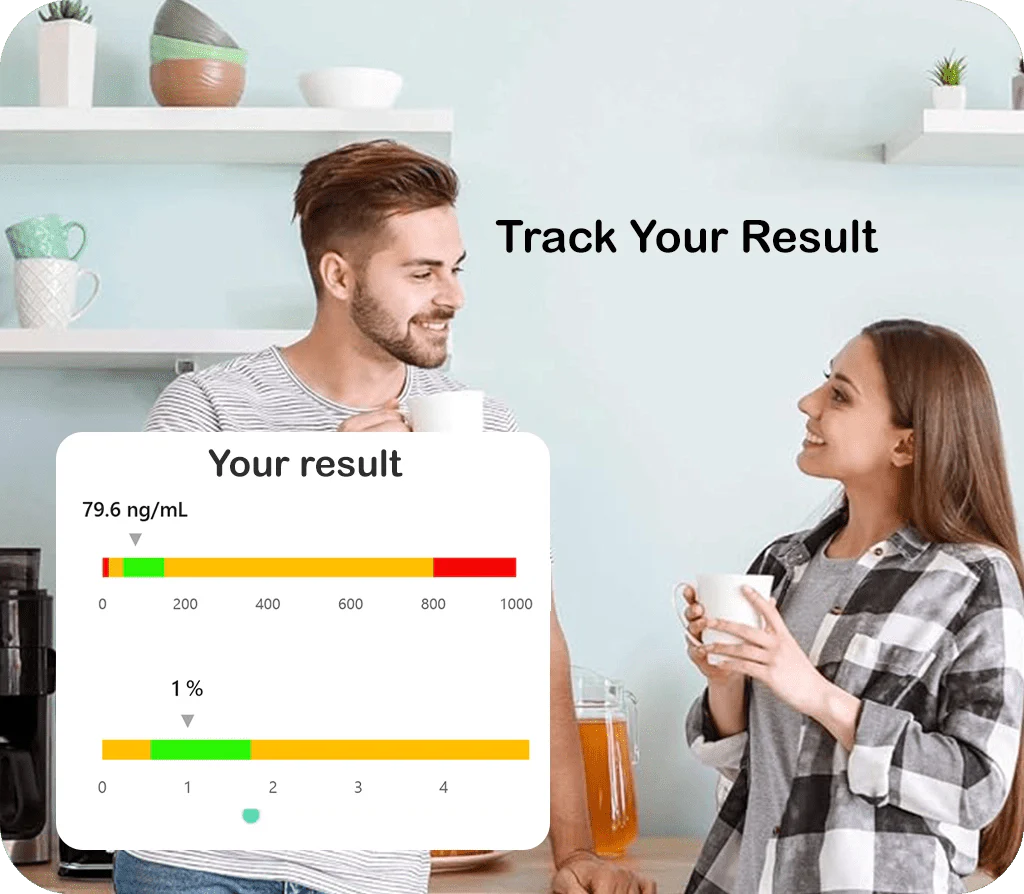
-
Anti-CCP
-
Rheumatoid Factor
-
Uric Acid
-
Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate

Why Core Rheumatology Assessment Matters?
Autoimmune and inflammatory conditions often develop gradually, with subtle symptoms that can be overlooked. This assessment provides valuable insights into your immune activity and inflammation levels, helping identify conditions like rheumatoid arthritis at an early stage. Early diagnosis can lead to more effective treatment, less joint damage, and improved long-term outcomes.
Why Choose Clinic-Based Blood Testing?
-
Accurate Results
Samples are collected by trained professionals for precise, lab-quality outcomes.
-

Fast Health Insights
Quick, In-clinic testing enables early detection and faster follow-up care.
-

Expert Oversight
Healthcare staff guide the process and help interpret your results.
-

Nationwide Access
Convenient locations across the UK through The National Phlebotomy Clinic.
FAQs
Collapsible content
What is Anti-CCP and why is it important?
Anti-CCP (anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide) antibodies are highly specific for rheumatoid arthritis and can appear before symptoms begin. Their presence can help confirm a diagnosis earlier than other markers.
How is rheumatoid factor different from Anti-CCP?
Rheumatoid factor is an older marker and may be elevated in other autoimmune or chronic infections, while Anti-CCP is more specific to rheumatoid arthritis and often indicates a more aggressive disease course.
Can high uric acid levels indicate arthritis?
Yes, elevated uric acid may suggest gout, a type of arthritis caused by crystal buildup in the joints, leading to sudden, painful inflammation.
What does ESR tell us?
Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR) is a general marker of inflammation. High levels suggest an inflammatory process in the body but do not point to a specific condition on their own.
Who should consider this test?
Anyone with unexplained joint pain, stiffness lasting more than a few weeks, morning joint discomfort, or a family history of autoimmune disorders may benefit from this screening.
Subscribe to our emails
Be the first to know about new collections and exclusive offers.